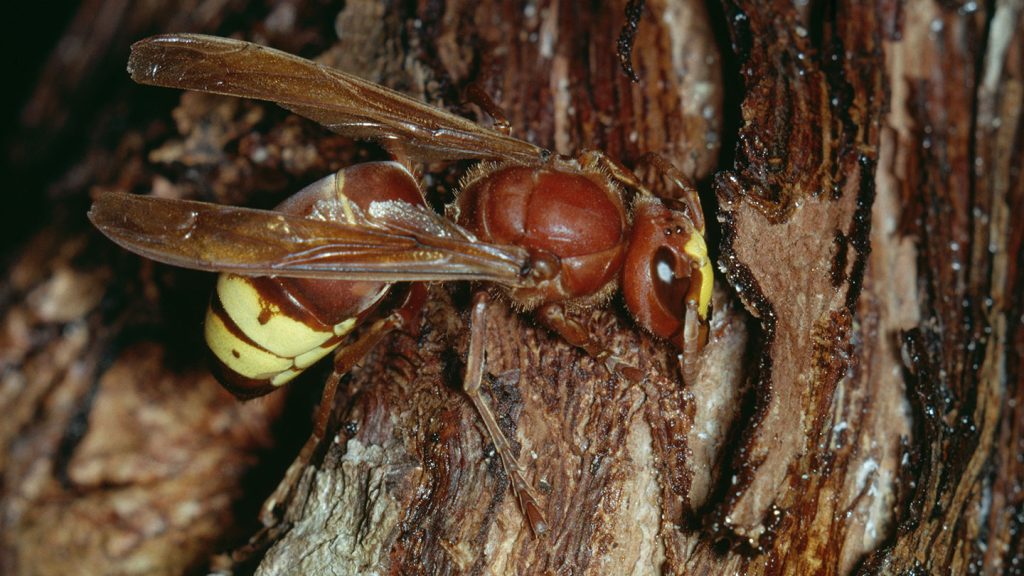
Researchers have discovered that Vespa orientalis hornets are able to consume large quantities of alcohol without any ill effects. In fact, these hornets can survive weeks of binging on sugared liquid that’s 80 percent ethanol, a feat unheard of in the animal kingdom. Tree shrews were previously believed to be the drinking champions due to their tolerance of alcohol in nectar, but the hornets have surpassed them in resistance to ethanol.
Interestingly, adult hornets encounter alcohol in nectar that is naturally spiked by plants or fruits beginning to ferment. Lab experiments involved feeding the hornets ethanol concentrations up to eight times higher than what would be lethal for other species. Surprisingly, the hornets showed no negative impacts from the binge drinking, with life spans remaining steady and nest-building behavior unaffected.
Researchers believe that the hornets’ ability to metabolize ethanol quickly may be attributed to the presence of fermenting yeasts in their guts. This fast detoxification process helps the hornets process the alcohol without any adverse effects, similar to how some human populations have evolved to tolerate high alcohol consumption. Additionally, the interaction between hornets and yeasts may play a role in creating the unique characteristics of wines, known as terroir.
Despite the challenges of studying drunkenness in large stinging insects, researchers were able to observe the hornets’ behavior under the influence of alcohol. Moving forward, researchers hope to explore how ethanol consumption affects hornet social interactions, tending of larvae, and the behavior of queens. By further studying the hornets’ ability to resist alcohol, researchers may gain insight into the evolution of tolerance to toxins in other animals.
The unexpected discovery of the hornets’ ability to withstand chronic alcohol consumption sheds light on the diverse ways that organisms have adapted to different environmental challenges. This research highlights the importance of studying lesser-known species and their unique adaptations, and how these findings can have broader implications for understanding biological processes. By investigating the mechanisms behind the hornets’ resistance to alcohol, researchers hope to unravel the mysteries of detoxification and tolerance in the animal kingdom.