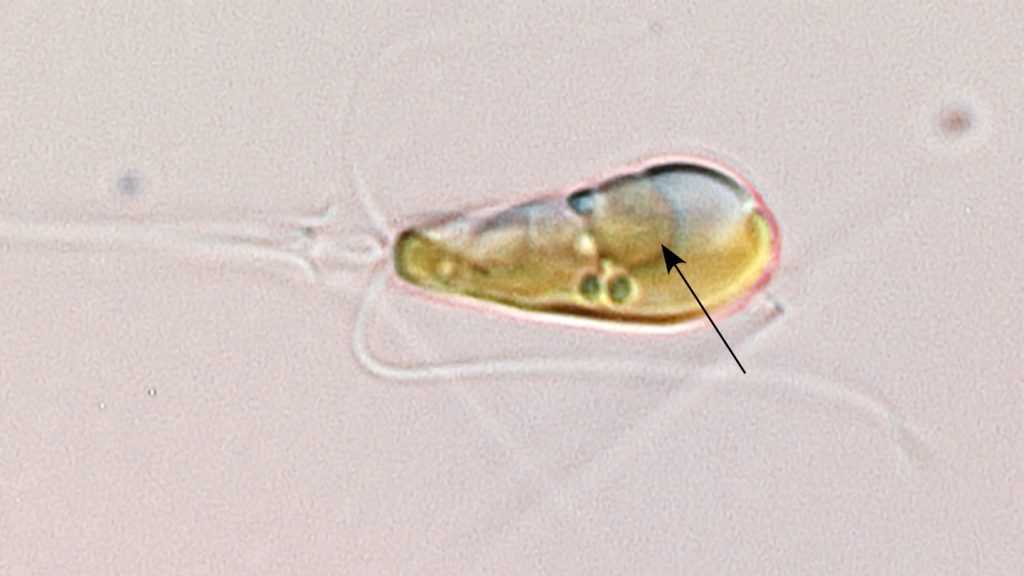
Researchers have discovered that a single-celled ocean alga has a special factory that allows it to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a biologically useful form. This was previously thought to be a process only done by bacteria and archaea. The presence of this ammonia factory in the alga indicates that eukaryotes, organisms with membrane-bound structures called organelles, are also capable of nitrogen fixation. The discovery was reported in the journal Science on April 12th.
The factory responsible for converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia in the alga was once a bacterium that began living inside the alga approximately 100 million years ago. Over time, this bacterium evolved into a nitrogen-harvesting machine for the host alga, becoming one of its organelles. This transformation from symbiont to organelle showcases the complexity of cellular evolution and the interdependent relationships between different types of organisms.
The process of nitrogen fixation is crucial for life as it converts atmospheric nitrogen gas into ammonia, which is essential for synthesizing biochemicals. Bacteria and archaea that have the capability of nitrogen fixation typically perform this process in soil or aquatic environments like the ocean. The presence of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as UCYN-A, in oceanic environments is important for marine ecosystems and contributes to the nitrogen cycle in the oceans.
Through X-ray imaging and genetic analyses, researchers were able to comprehend the relationship between the alga and the UCYN-A symbiont. The symbiont, known as a nitroplast, participates in cellular processes within the alga, dividing in synchronization with other organelles. Genetic information revealed that the symbiont relies on the host alga for essential metabolic pathways, indicating a coevolutionary relationship between the two organisms.
The presence of special amino acid chains in the proteins of the UCYN-A bacterium suggests a sophisticated trafficking mechanism within the cell, akin to other organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. The research highlights the evolution of symbionts into organelles, as seen in the nitroplast, providing insights into the mechanisms by which symbiotic relationships can lead to the domestication of bacteria within host cells. This process sheds light on the evolutionary history of organelles and their role in cellular function.
The emergence of the nitroplast as an organelle provides a unique case study in the evolution of symbiotic relationships within eukaryotic cells. The interdependence between the alga and the UCYN-A bacterium showcases the intricate processes involved in cellular evolution and the adaptation of symbionts into essential components of host cells. This discovery adds to our understanding of the diversity and complexity of cellular life and the mechanisms by which organisms have evolved to thrive in different environments.