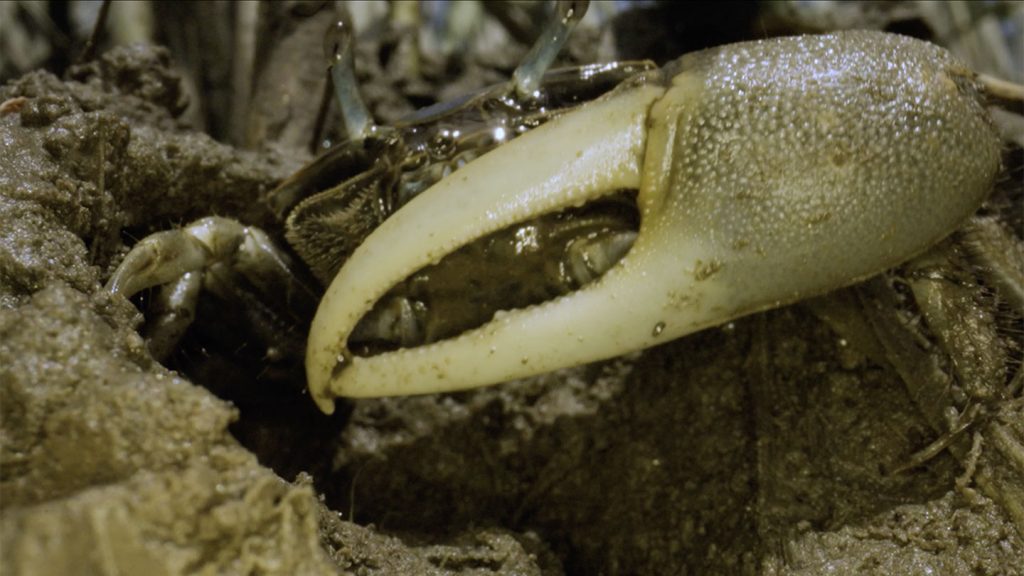
David Johnson studies the effect of climate change on marine invertebrates and coastal ecosystems in the Great Marsh. This area is the largest remaining swamp marsh left in New England and provides important services such as acting as nursery grounds for fish and supporting shell fishing and birding activities. Water in the Gulf of Maine is warming faster than almost anywhere else on the planet, leading to an increase in warm water species. Johnson has discovered a new species of crab, the purple marsh crab, which poses a threat to the marsh ecosystem due to its destructive feeding habits.
The fiddler crabs, which Johnson has been studying, have been found to reduce the amount of grass in the Great Marsh by 40 percent. This is in contrast to what is observed south of Cape Cod, where the presence of fiddler crabs helps plant growth. Fiddler crabs have been shown to have an impact on the marsh’s ability to keep up with sea level rise by reducing the amount of biomass that traps mud, which is essential for building up the marsh over time. Salt marshes help in storing carbon, and any disturbance to their ecosystems can release stored carbon back into the atmosphere.
In addition to studying the impact of fiddler crabs on the marsh ecosystem, Johnson is also monitoring the presence of other climate migrants, such as the blue crab and the purple marsh crab. While these species have shown up in the area, their impact on the local economy and ecology is still uncertain. Johnson emphasizes the importance of continued monitoring to understand the long-term impacts of these climate migrants on the Great Marsh. The rate of climate migrations is accelerating, and it is important to track these changes to predict their effects on the local ecosystems.
Salt marshes store more carbon than almost any other ecosystems on Earth, making them crucial for mitigating climate change. However, any disruption to the marsh ecosystem, such as the introduction of new species like the fiddler crabs, can lead to the release of stored carbon back into the atmosphere. Johnson and his team are working to understand the effects of these climate migrants on the marsh’s ability to store carbon and adapt to changing environmental conditions. The future of the Great Marsh and its inhabitants is uncertain, but ongoing research and monitoring are essential to ensure its long-term sustainability.