Summarize this content to 2000 words in 6 paragraphs
As we age, our bodies slow down — not just in how we move, but also at the cellular level, where a decline in protein mobility may contribute to the development of chronic health issues.
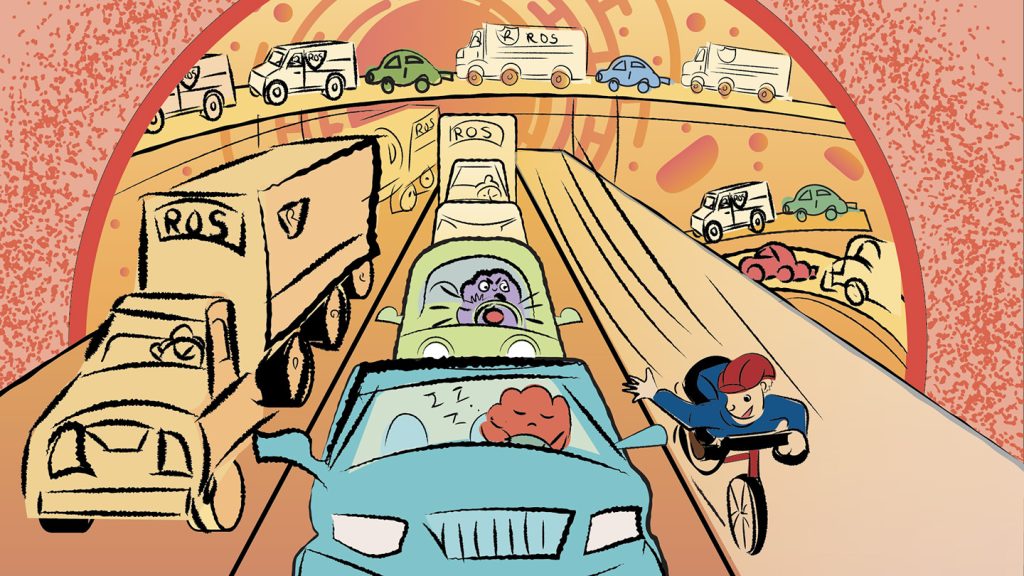
Molecular stress brought on by diabetes, fatty liver disease and other chronic conditions can all cause proteins to put on the brakes. Instead of zipping around the cell and bumping into each other to perform vital tasks, these proteins become ensnared in chemical traffic jams, creating a kind of widespread sluggishness termed “proteolethargy.”
Have feedback for Science News?
Help us improve by telling us about your experience
Such lethargy occurs when proteins with a sticky building block on their surface interact with harmful by-products from chronic inflammation and stress, causing the proteins to clump together and crawl to a near standstill, researchers report November 27 in Cell.
The result: Cells struggle to function, triggering the collapse of crucial biological systems — a hallmark feature of aging-related maladies.
This molecular bottleneck may be a “common denominator” underpinning many of life’s ailments, says cell biologist Alessandra Dall’Agnese, of the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research in Cambridge, Mass. “It’s a unifying mechanism.”
Nearly half of all proteins in the body carry the sticky residue implicated in protein malfunction, putting countless cellular processes — metabolism, cell repair, immune defense, gene regulation and more — at risk of grinding to a halt.
Antioxidants and drugs that counteract the stickiness of proteins can partially restore protein mobility, Dall’Agnese and her colleagues note in the paper. The findings could pave the way for therapies designed to ease these molecular roadblocks and tackle the root causes of chronic disease.
Questions or comments on this article? E-mail us at [email protected] | Reprints FAQ
We are at a critical time and supporting climate journalism is more important than ever. Science News and our parent organization, the Society for Science, need your help to strengthen environmental literacy and ensure that our response to climate change is informed by science.
Please
subscribe to Science News and add $16 to expand
science literacy and understanding.