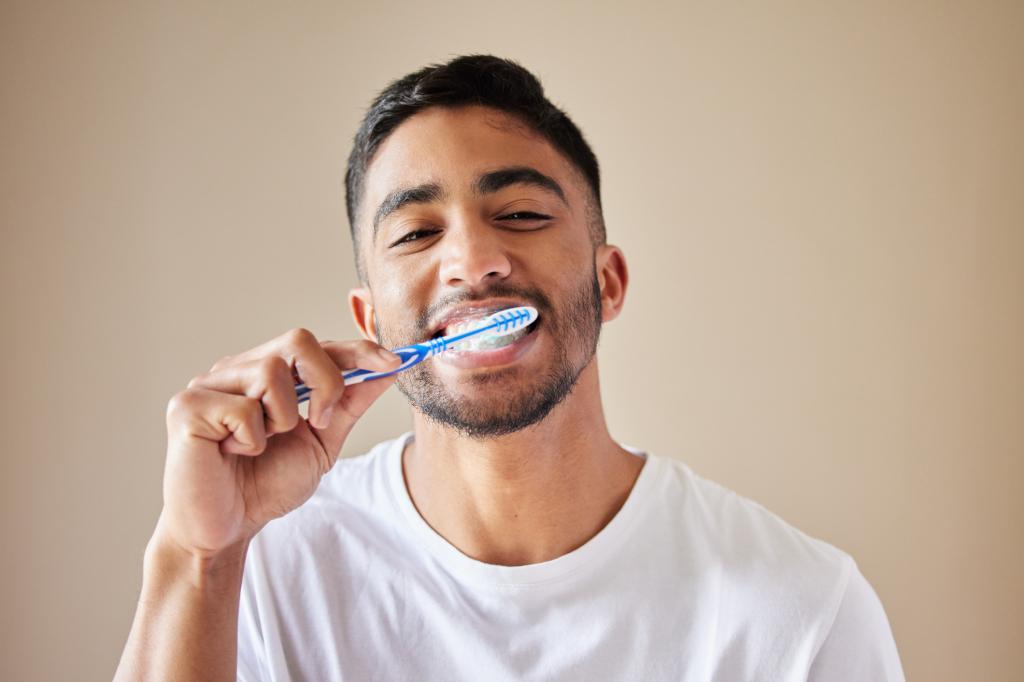
Dental experts are now advising Americans to stop rinsing their mouth after brushing their teeth in order to maximize the benefit of the fluoride in the toothpaste. Brittany Seymour of the American Dental Association and Harvard School of Dental Medicine recommends brushing teeth with fluoride toothpaste twice a day without rinsing afterwards. Margherita Fontana of the University of Michigan School of Dentistry explains that rinsing immediately after brushing washes away the active ingredients of the toothpaste, reducing its effectiveness. Instead of rinsing immediately, it is suggested to wait 20 minutes or just take a tiny sip of water if necessary.
A study conducted in 1999 found that teenagers who rinsed their mouth less after brushing had fewer cavities and decaying teeth compared to those who rinsed thoroughly. The residual fluoride left in the mouth from the toothpaste was found to be beneficial for dental health. Children need to be monitored when using fluoride toothpaste to prevent them from swallowing it. For children under three, only a smear of toothpaste the size of a rice grain is recommended, while children ages three to six can use a pea-sized amount. Pediatric dentist Scott Cashion advises children to spit out toothpaste and avoid rinsing to allow the fluoride to protect their teeth overnight.
Drinking excessive amounts of water or other liquids throughout the day can also be detrimental to dental health, according to Texas-based dentist Dr. Ellie Phillips. She explains that constantly sipping on liquids leads to a dilution of saliva, which is the mouth’s most healing liquid. Saliva contains proteins that protect tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay, making it essential for oral health. By consuming large quantities of water, the benefits of saliva are reduced, ultimately compromising dental health. It is recommended to avoid excessive water consumption and allow saliva to do its job in protecting teeth and gums.
Educating people about the importance of maintaining the residual fluoride from toothpaste in the mouth and minimizing rinsing after brushing can lead to improved dental health outcomes. The guidance from dental experts to rinse minimally or wait for some time before rinsing can help individuals derive maximum benefit from their oral hygiene routine. Monitoring children’s use of fluoride toothpaste and teaching them to spit without rinsing can also contribute to better dental health outcomes during childhood and beyond. Additionally, avoiding excessive water consumption throughout the day can help preserve the benefits of saliva and protect tooth enamel from decay.
By incorporating these recommendations into their daily oral hygiene routine, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their dental health. Understanding the role of fluoride in toothpaste, the importance of salivary proteins, and the potential risks of excessive water consumption can empower people to make informed choices about their oral care. Implementing these practices can lead to reduced cavities, healthier teeth, and overall better oral health outcomes for both children and adults. Continued education and awareness about these oral health practices can help individuals prioritize and maintain their dental health throughout their lives.