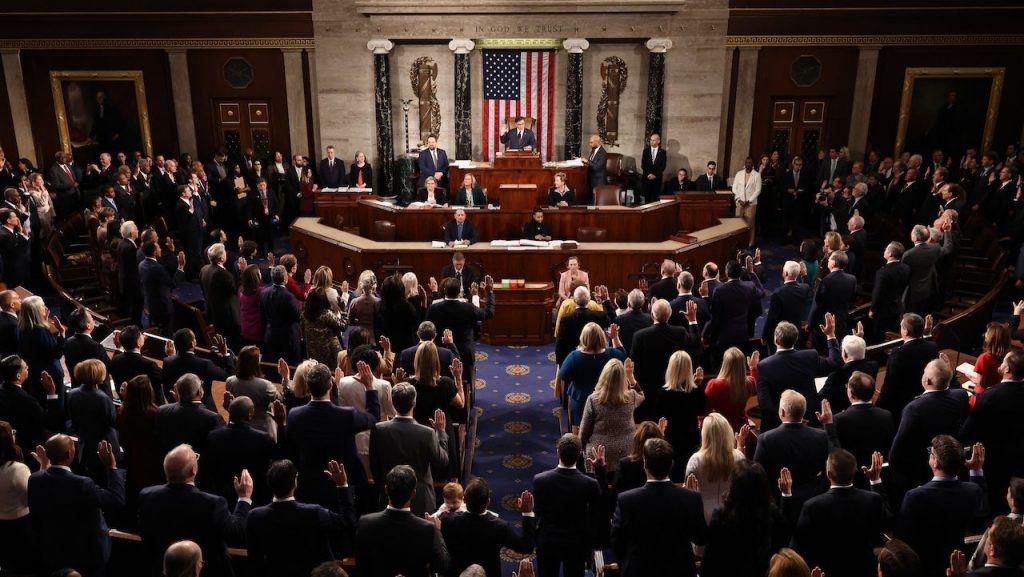
The Joint Session of Congress to certify the results of the 2024 presidential vote is set to take place on Monday. Security measures have been heightened since the Capitol riot, with 10-foot-high fencing being erected around the Capitol complex. Vice President Harris, who presides over the session, is in the unique position of certifying her own defeat in the election. The process is outlined in the 12th Amendment to the Constitution, with the House and Senate convening together to receive and count the electoral votes.
Changes to the Electoral Count Act were made in late 2022, clarifying the Vice President’s role in the certification process. The law states that the Vice President’s role is “ministerial” and does not give them the power to adjudicate disputes over electors or votes. An expedited judicial appellate process was also established for electoral vote litigation, and the process for contesting a state’s electors during the Joint Session was altered. The old system required one House member and one senator to challenge a state’s electoral slate, but now it requires more members from both chambers to do so.
The outcome of the 2024 election is not in dispute, and there is no expectation of additional Congressional reviews of the Electoral College. Despite additional security precautions, officials are not anticipating rallies or violence during the certification process this year. During the certification of the 2020 election in 2021, Vice President Pence certified the outcome of the electoral vote, and this year’s process is expected to be completed in about an hour. Following the certification, Donald Trump will be announced as the winner of the election for a second term beginning on January 20, 2025.
In the past, other Vice Presidents, such as Richard Nixon and Al Gore, have presided over the certification of their own defeat in the presidential election. The 2022 Electoral Count Act reforms solidified the Vice President’s role in the certification process, making it clear that they do not have the authority to resolve disputes over electors or votes. The updated law also made it more difficult to challenge a state’s electoral certificates, requiring a larger number of members from both chambers to do so.
The Joint Session of Congress is where the House and Senate convene together to certify the election outcome, and this year’s session will be presided over by House Speaker Mike Johnson. The process will involve the tabulation of the electoral votes, beginning with the state of Alabama. The certification process will culminate in Vice President Harris announcing Donald Trump as the winner of the election for a second term. The session is expected to run smoothly and be completed within a short timeframe, unlike the events of the previous year.