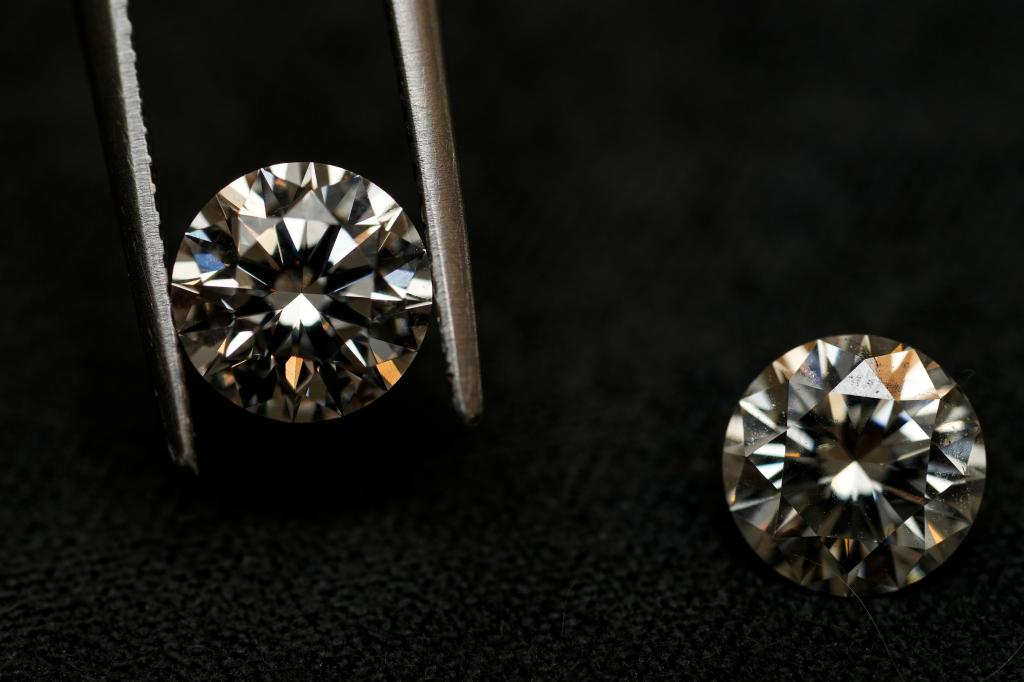
Scientists have developed a faster method of creating diamonds in a laboratory setting, significantly reducing the time it takes to produce the precious stones. Rodney Ruoff, a materials scientist, and his team have successfully created a lab-grown diamond in just 3 hours, compared to the usual 10 weeks required for traditional methods. The researchers experimented with different conditions to find the ideal circumstances for diamond formation, ultimately leading to their breakthrough discovery. The study, published in the journal Nature, outlines the process of creating diamonds using a mixture of liquid gallium, nickel, silicon, and iron heated to high temperatures and exposed to specific gases.
The team found that by combining silicon and carbon gas, they were able to bond carbon atoms and create tiny crystals that eventually formed a diamond. This process was completed in just 150 minutes, marking a significant advancement in lab-grown diamond production. While the initial diamonds created were minuscule in size, there is potential for larger gems to be produced in the future. Ruoff predicts that other scientists will soon replicate their methods and begin producing their own lab-grown diamonds, leading to a potential increase in availability and affordability of these gemstones. The discovery comes at a time when lab-grown diamonds are becoming increasingly popular due to their ethical considerations and cost-effectiveness.
The rise of lab-grown diamonds is occurring within the jewelry industry as more consumers opt for these sustainable alternatives over natural diamonds. In response to the growing demand for lab-grown diamonds, jewelers are starting to incorporate them into engagement rings and other jewelry pieces. Many consumers prefer lab-grown diamonds for their affordability and ethical sourcing, as they avoid the environmental and social concerns associated with traditional diamond mining. Some experts predict that lab-grown diamonds may soon outsell natural diamonds in the engagement ring market, further highlighting the shift towards more sustainable and accessible gemstones.
As the technology for creating lab-grown diamonds advances, it is expected that the production of larger diamonds will become more feasible, allowing for greater customization and availability in the market. The ability to create diamonds quickly and efficiently in a controlled laboratory environment presents numerous opportunities for innovation and growth within the jewelry industry. With more labs around the world likely to adopt similar techniques for producing lab-grown diamonds, the market for these gemstones is expected to expand further. Overall, the development of faster and more efficient methods for creating lab-grown diamonds represents a positive step towards sustainability and ethical sourcing in the jewelry industry.