A Toronto-based registered dietitian recently assessed the health effects of Coke Zero and Diet Coke, both of which contain aspartame, caffeine, natural flavors, and caramel colors. While both these sweeteners have been deemed safe, some concerns have been raised about the possible carcinogenic effects of aspartame. Despite this, the Food and Drug Administration disagrees with these claims, emphasizing that aspartame is not linked to cancer. The acceptable daily intake for aspartame is up to 50 milligrams per kilogram of body weight per day. Ace-K is another sweetener found in Coke Zero and is regulated by the FDA as a food additive.
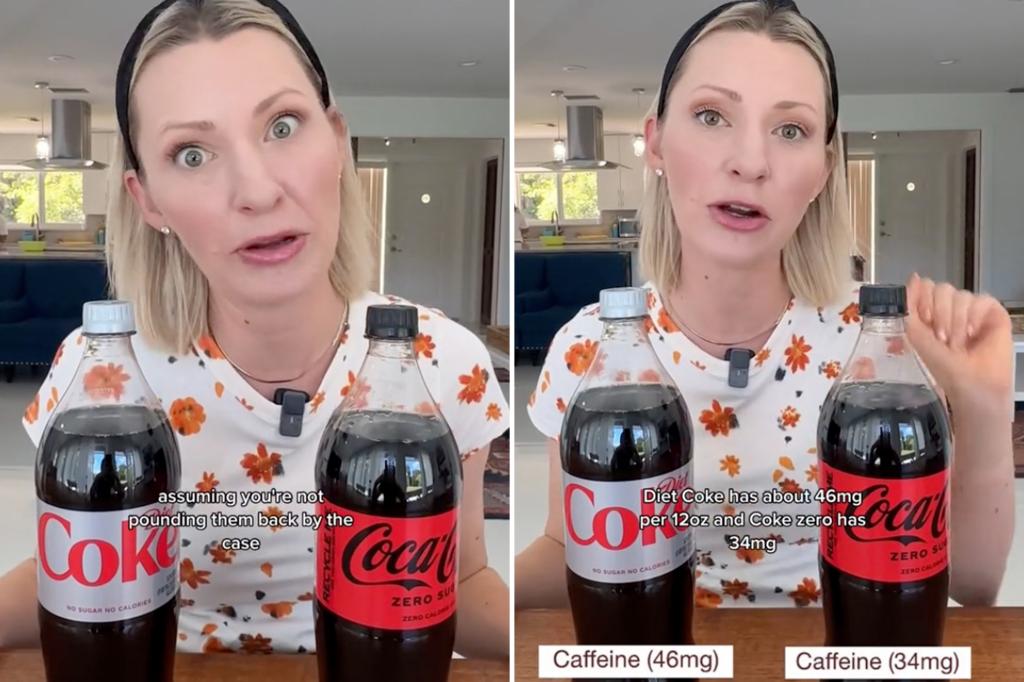
A French study from 2022 linked aspartame to an increased risk of stroke and Ace-K to a higher risk of coronary artery disease. Diet Coke and Coke Zero also differ in terms of caffeine content, with Diet Coke having about 46 milligrams in a 12-ounce can and Coke Zero having 34 milligrams. Despite these differences, both drinks fall under the category of diet sodas which should be consumed in moderation. It is noteworthy that artificial sweeteners may lead the body to crave more sweets as they do not raise blood glucose levels but can trigger an increase in insulin levels in the body over time.
The debate between Diet Coke and Coke Zero preferences varies among consumers with some favoring the taste of Coke Zero while others prefer Diet Coke due to its lack of an aftertaste. Some individuals do not care for either soda and mentioned that cherry Coke Zero was not terrible. Ultimately, the decision between the two comes down to personal preference, and both should be consumed in moderation. It is important to realize that diet sodas are not considered health foods, and they should be treated similarly to regular, full-sugar sodas.
Overall, the findings related to the health effects of Coke Zero and Diet Coke suggest that while there may be some concerns about the sweeteners used in these sodas, they have been deemed safe for consumption in modest amounts. The FDA has reviewed numerous studies on aspartame and Ace-K, reassuring consumers of their safety. As with any food or beverage, moderation is key when it comes to consuming diet sodas, and individuals are encouraged to choose the option that they enjoy the most. The impact of artificial sweeteners on the body’s insulin levels should also be considered when deciding whether to consume diet sodas regularly.