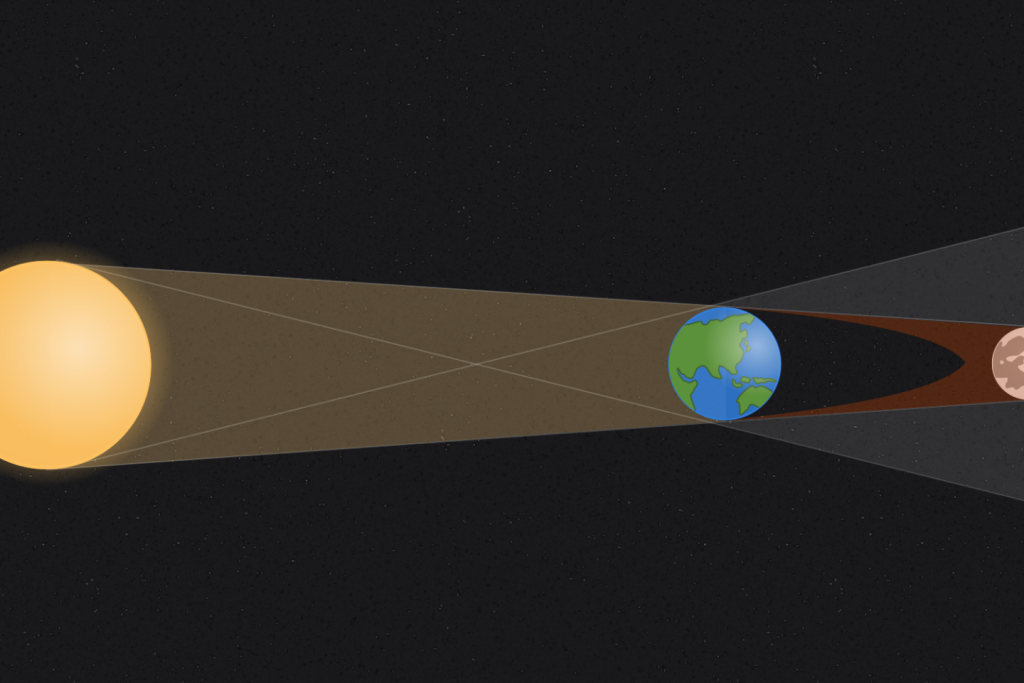
Eclipses, everyone can explain to you, occur when the Moon, Earth, and Sun align and our planet and its companion cast shadows on each other: in one case, the Moon obscures the Sun, and the eclipse is solar; in the other, it is the Moon that passes into the Earth’s shadow, and the eclipse is lunar. There are three types of solar eclipses that can be observed: total, partial, and annular. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon completely covers the Sun, allowing observers to see the Sun’s atmosphere. Partial solar eclipses occur when the Moon only partially covers the Sun, and annular solar eclipses happen when the Moon is too far from the Earth to completely block out the Sun.
In comparison, lunar eclipses are less well-known but can be longer than solar eclipses because the Earth’s shadow that the Moon enters is much wider. Lunar eclipses can be penumbral, partial, or total. During a penumbral eclipse, the Moon does not enter the Earth’s shadow but rather its penumbra, resulting in a slight darkening of the lunar surface. Partial lunar eclipses occur when part of the Moon is obscured by the Earth’s shadow, while total lunar eclipses happen when the entire Moon enters the Earth’s shadow and takes on a reddish tint known as the “blood Moon.”
The frequency of eclipses is limited because of the inclination of the Moon’s orbit around the Earth relative to the Earth-Sun plane. The Moon’s orbit crosses this plane at two points, known as lunar nodes, and if the Moon aligns with the Earth and Sun when passing over one of these nodes, an eclipse occurs. Despite the Moon completing its orbit around the Earth in about 29.5 days and aligning with the Earth and Sun during this time, eclipses are less frequent due to this inclination. As the Moon continues to move away from the Earth at a rate of 3 centimeters per year, total solar eclipses will eventually disappear in about 650 million years.
It is important to note that observing solar eclipses can be dangerous without proper eye protection, as the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet and infrared rays can cause irreversible eye damage. Therefore, it is essential to use appropriate protective eyewear when viewing such events. Lunar eclipses are also a fascinating natural phenomenon to observe, with the “blood Moon” being a unique and beautiful sight during a total lunar eclipse. While eclipses may seem rare, they are a regular occurrence due to the alignment of the celestial bodies in our solar system.
Overall, eclipses are awe-inspiring events that offer a glimpse into the workings of the celestial bodies in our solar system. From the alignment of the Moon, Earth, and Sun during a solar eclipse to the various types of lunar eclipses, each event provides a unique opportunity to observe and learn more about the universe. As technology and scientific advancements continue to improve, our understanding of eclipses and other astronomical phenomena will also deepen, allowing us to appreciate the beauty and complexity of our cosmos even further.