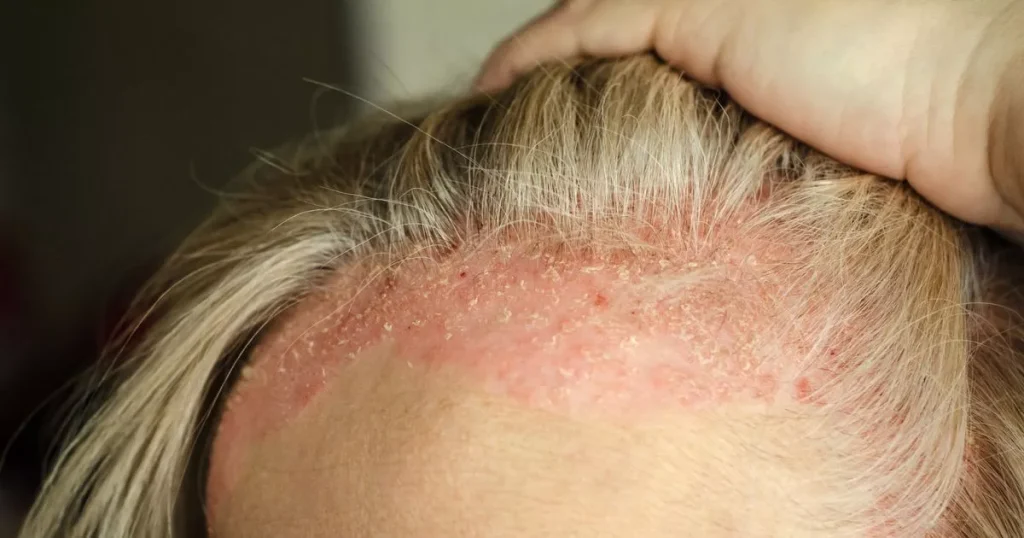
Atopic eczema is a common skin condition that often occurs in people with allergies, with one third of children with atopic eczema developing asthma or hay fever as well. The skin in affected areas is red, dry, itchy, and can sometimes weep, blister, crust, or scale. The exact causes of atopic eczema are unknown, but there is believed to be a genetic component, with symptoms often running in families. Food allergies can also play a role, and patients may be asked to keep a food diary to identify trigger foods. The main symptom is itchiness, with commonly affected areas being the elbows, knees, wrists, and neck. Some research suggests that dietary changes and vitamin D supplementation may help improve symptoms.
Eczema affects approximately one in five children, and there are simple steps that can be taken to improve symptoms. In a 2013 study, low vitamin D levels during pregnancy and childhood were linked to an increased risk of developing eczema. A 2020 trial found that vitamin D supplementation reduced eczema severity in patients. Foods rich in vitamin D, such as cod liver oil, sardines, salmon, and eggs, may help prevent eczema in children and adolescents. However, it’s important to be cautious of allergens – if certain foods trigger eczema flare-ups, they should be avoided. Consulting a GP for advice is recommended.
Eczema treatment can involve lifestyle changes, such as avoiding trigger foods and incorporating foods rich in vitamin D. Keeping the skin hydrated and moisturized can also help alleviate symptoms. Vitamin D supplementation may be helpful, especially for those with low levels of the vitamin. In severe cases, medical treatment may be necessary, including topical corticosteroids or immunosuppressants. Avoiding irritants, allergens, and harsh chemicals in skincare products can also help manage eczema.
Sunscreen is an important part of skincare for people with eczema, as sun exposure can worsen symptoms. Opting for sunscreens with ingredients suitable for sensitive skin is advisable. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can also help manage symptoms of eczema. Stress management techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or yoga may be beneficial as stress can exacerbate eczema. Getting enough sleep and staying hydrated are also important factors in managing eczema.
Research suggests that a balanced diet, rich in vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, may help prevent eczema and improve symptoms. Avoiding trigger foods and irritants, as well as keeping the skin moisturized and protected from sun exposure, are key components of eczema management. Vitamin D supplementation has shown promising results in reducing eczema severity, and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise and stress management, can also contribute to improved skin health. Consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice on eczema treatment is recommended for optimal care.