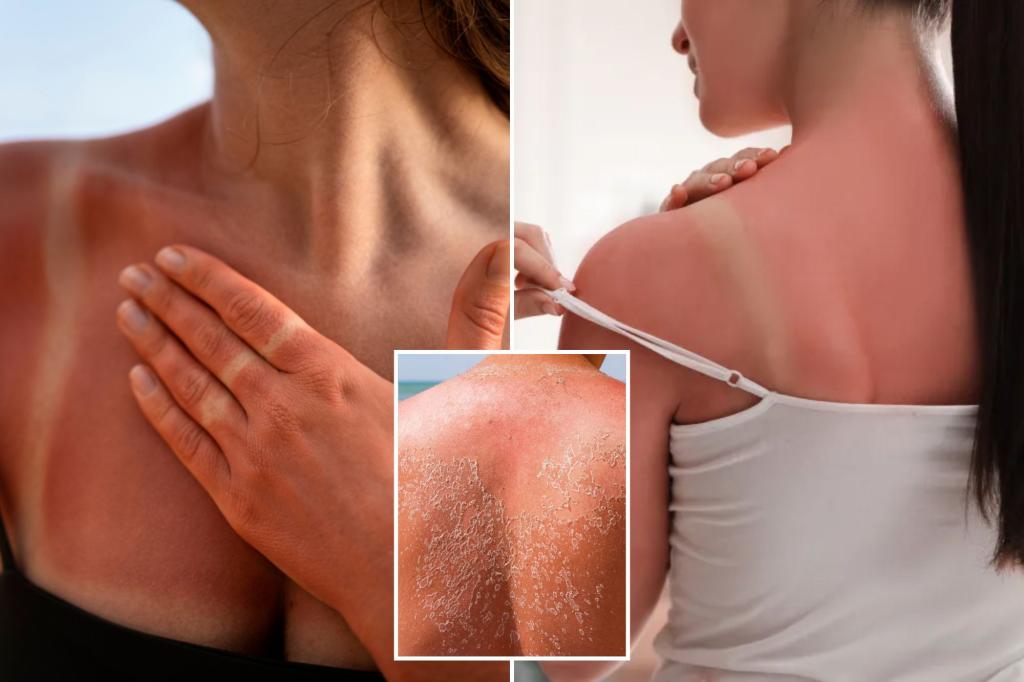
One-third of adults are expected to experience at least one sunburn this year, with white adults under 30 being the most affected group. More than 33,000 sunburn cases will require a trip to the emergency room, and sunburn also increases the risk of developing skin cancer. Health experts are highlighting the differences between sunburn and sun poisoning, with both conditions resulting from prolonged sun exposure without proper protection.
Dr. Anisha Patel, an associate professor of dermatology, explains that while sunburn and sun poisoning may look similar, the latter is typically more intense and can involve symptoms like swelling and blisters. The key differences lie in the systemic symptoms, such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, and a rapid heartbeat. Harvard Health notes that a mild to moderate sunburn is characterized by redness, pain, and hot skin, which typically clears up within three days. On the other hand, sun poisoning presents with more severe symptoms like blisters, severe pain, swelling, and fever that linger longer.
Individuals at a higher risk of sun poisoning include babies, children, those with fair skin or skin conditions, outdoor workers during peak sun hours, individuals on certain medications, indoor tanning-bed users, and those who do not take proper sun precautions. Experts advise individuals who have been sunburned to get out of the sun, drink plenty of water, rest, and manage pain with medication like ibuprofen. Other recommended treatments include applying cool compresses, aloe vera gel, fragrance-free creams, or taking a cool bath with colloidal oatmeal. Avoid popping blisters or using cortisone on the skin, as these can slow down the healing process.
Medical attention should be sought if sunburn symptoms worsen, including bright red, oozing skin, fever, mental confusion, severe pain, extreme cold sensations, headache, nausea, or vomiting. Sun poisoning requires prompt medical assessment to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. Prevention is crucial in avoiding sunburn and sun poisoning, with individuals advised to use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, seek shade during peak sun hours, and avoid indoor tanning beds. It is essential to be aware of one’s risk factors for sunburn and take appropriate precautions to protect against harmful UV radiation.