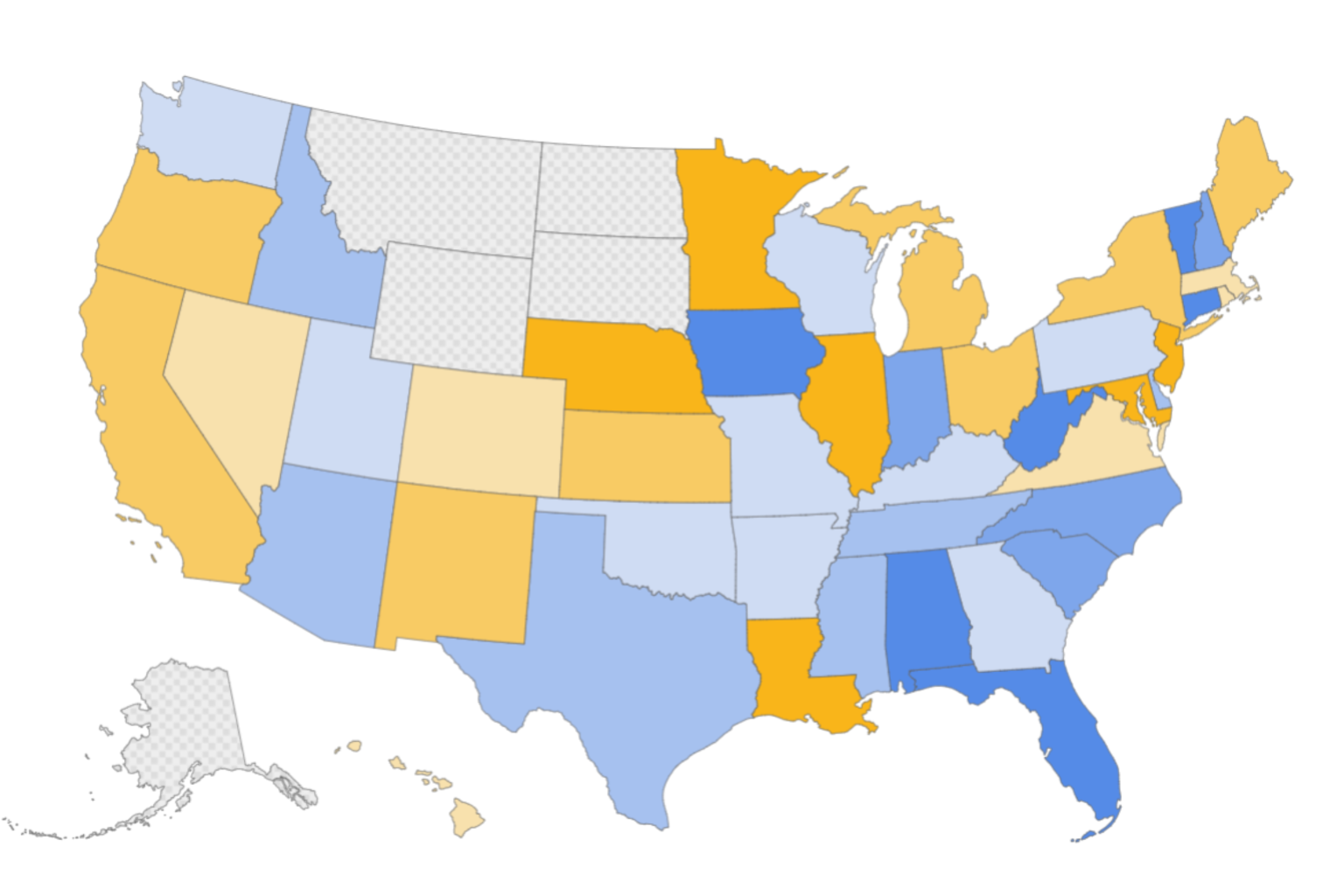
A study analyzing U.S. Census Bureau data conducted by HireAHelper.com found that high-income households are less likely to move compared to lower-income brackets, but when they do, they tend to relocate to different states. In 2023, only 6.5 percent of the top earners moved, while 9 percent of the bottom 20 percent moved. The top earners were defined as those with an annual income of $150,000 or more. Vermont emerged as the most popular destination for high earners, with a net gain of 89 percent in this income bracket. Other states like West Virginia, Connecticut, and Iowa also attracted a significant influx of wealthy households.
The migration of high-income individuals to different states can have significant economic impacts. It brings substantial financial resources to their new states, stimulating local economies by increasing demand for housing, services, and luxury goods. This influx can drive up property values and living costs. Conversely, states losing high earners like California and New York face economic challenges, including declining tax revenues. In 2023, California and New York collectively lost $90 billion in income tax revenues due to out-migration of wealthy residents.
High earners have various motivations behind their moves. They often cite upgrading to better housing and job opportunities as reasons for relocating. Owning a home was nearly five times more common among high earners compared to lower-income individuals. In contrast, lower-income Americans are more likely to move for cheaper housing, health reasons, and family considerations. The movement of high and low earners can impact broader trends such as gentrification and poverty concentration, reshaping the demographic and economic landscape of the country.
The study highlighted states like Vermont, West Virginia, Connecticut, and Iowa as popular destinations for high earners due to factors such as quality of life, natural beauty, lower costs of living, and tax benefits. The influx of high earners can lead to development and job growth in communities, but it can also drive up housing prices, causing challenges for lower-income residents. The movement of high earners based on income is reshaping the economic and demographic landscape of the country, impacting states differently based on their tax policies, living costs, and desirability to wealthy individuals.
States like California and New York are facing economic challenges due to the out-migration of high earners, resulting in declining tax revenues. On the other hand, states like Vermont and West Virginia are attracting an influx of wealthy households, stimulating their local economies. The movement of Americans based on income can have broader societal implications such as gentrification, poverty concentration, and educational disparities. Understanding these migration patterns is essential for policymakers to address economic disparities and ensure balanced growth across states.