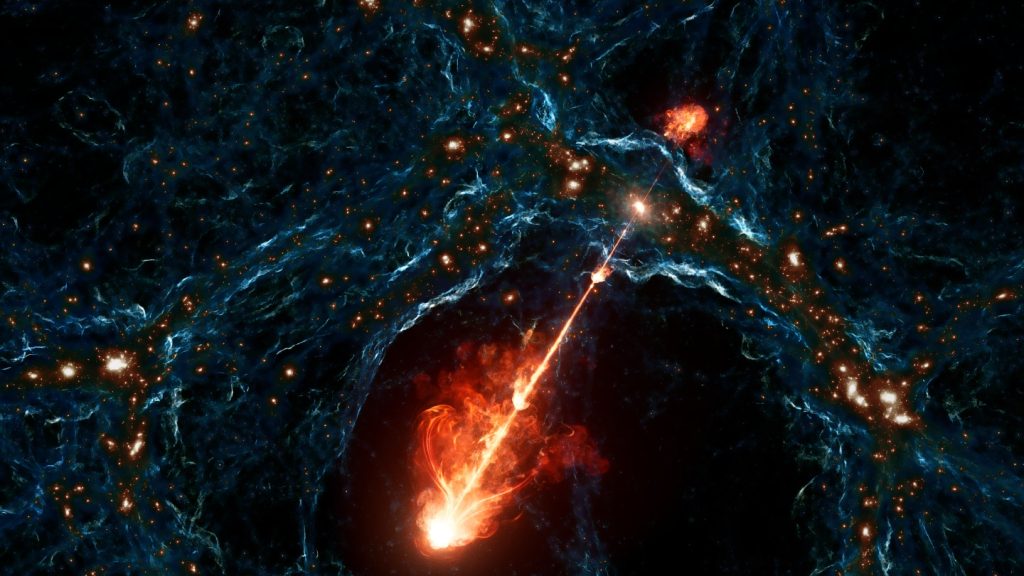
Astronomers have discovered the longest pair of black hole jets ever seen, spanning 23 million light-years, with implications for the evolution of the universe on cosmic scales. Traditionally, astronomers believed that all jets remain within, or close to, their host galaxy, but this discovery challenges that notion by suggesting that supermassive black holes can also influence the surrounding cosmic web. Named Porphyrion, this pair of jets was observed with the LOFAR network in the Netherlands, outstretching the previous record holder by 7 million light-years, hinting at their potential to influence beyond galaxies.
Porphyrion is believed to be embedded in a filament of the cosmic web, where most of the universe’s ordinary matter resides. Follow-up observations indicate that the jets existed at an early stage of the universe’s history when cosmic filaments were closer together, showcasing their capacity to span large distances across voids between the filaments. The discovery of Porphyrion highlights the potential for black hole jets to have a significant influence on cosmic structures and evolution, challenging previous assumptions about the reach of these phenomena.
Citizen science efforts to identify large black hole jets have revealed over 10,000 systems that span at least 3 million light-years, although none have been as extensive as Porphyrion. This suggests that such large black hole jet systems may be more common than previously thought, indicating a potentially larger influence on cosmic evolution than expected. The discovery of these massive black hole jets opens up new avenues for understanding the role of supermassive black holes in shaping cosmic structures and processes, shedding light on the interconnectedness of galaxies and the cosmic web.
The findings from these observations provide valuable insights into the intricate connections between galaxies, supermassive black holes, and the cosmic web, offering a glimpse into the complex interplay of cosmic forces at play. By studying these massive black hole jets and their influence on cosmic structures, astronomers can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms driving the evolution of the universe on a grand scale. The discovery of Porphyrion and its implications highlight the importance of ongoing research efforts to further unravel the mysteries of the cosmos and the role of supermassive black holes in shaping the cosmic landscape.