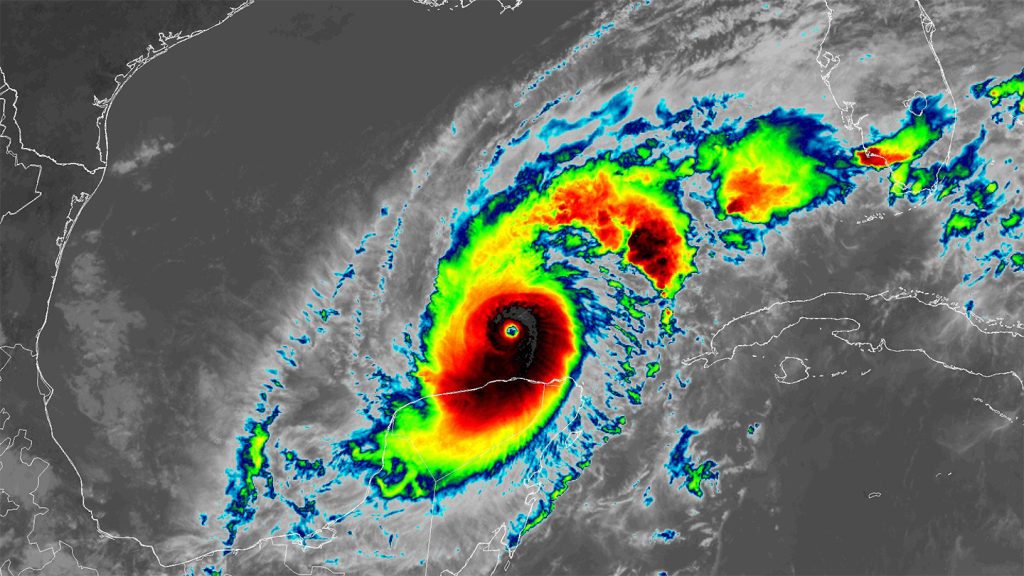
Two recent reports have highlighted the impact of human-caused climate change on extreme weather events. For Hurricane Helene, the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico played a significant role in its rapid growth and intensity. The storm was fueled by the warm seawater, which allowed it to absorb heat and release it into the storm core as humid air. The storm’s movement caused more heat and water to be pumped into the air, resulting in faster winds. Additionally, Helene’s relatively compact size compared to another storm named Milton may have contributed to its explosive growth. The warm Gulf waters were found to be significantly warmer due to climate change, making the high temperatures along Helene’s path 200 to 500 times more likely.
The World Weather Attribution initiative conducted an analysis of the impact of climate change on Hurricane Helene’s intensification and the resulting rainfall as it moved inland across the Southern Appalachian Mountains. Gulf of Mexico sea surface temperatures were found to be about 1.26 degrees Celsius warmer than they would have been in a world without climate change. This anomaly made the high temperatures along Helene’s path 200 to 500 times more likely. The storm dumped 20 to 30 inches of rain in some parts of Appalachia, which was approximately 10 percent heavier due to human-caused climate change. This heavy rainfall led to flooding and hundreds of deaths across the U.S. Southeast.
Climate Central also contributed to the analysis of sea surface temperatures in the Gulf for Hurricane Helene. The group reported that the elevated sea surface temperatures in the southwestern Gulf of Mexico also contributed to the rapid intensification of Hurricane Milton. These warm waters were made 400 to 800 times more likely over the past two weeks due to human-caused climate change. Due to Hurricane Helene’s impact, the National Centers for Environmental Information data repository was temporarily knocked out, leading Climate Central to use sea surface temperature data from the European Union’s Copernicus Marine Service. Climate scientist Daniel Gilford emphasized that climate change is happening now and influenced both of these storms to the extent that they did, with dramatic consequences that should be taken note of.
The reports highlight how researchers can estimate the likelihood or severity of past natural disasters due to human-caused climate change. The data shows the significant influence of climate change on extreme weather events like Hurricane Helene and Hurricane Milton, showcasing the importance of acknowledging and addressing climate change impacts. The warmer sea surface temperatures in the Gulf of Mexico due to climate change have been demonstrated as a key factor in the intensification and rapid growth of these storms. By understanding and recognizing the role of climate change in extreme weather events, steps can be taken to mitigate its impacts and work towards a more sustainable future.
The findings from the reports emphasize the urgency of addressing climate change and its impact on extreme weather events. The influence of climate change on hurricanes and tropical storms is becoming increasingly evident, with warmer sea temperatures creating more favorable conditions for the rapid intensification of storms. The environmental consequences of this phenomenon are far-reaching, leading to heavier rainfall, flooding, and other negative impacts on communities and ecosystems. By raising awareness and taking action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to a changing climate, the potential for future extreme weather events like hurricanes can be mitigated, protecting lives and livelihoods.
In conclusion, the reports on Hurricane Helene and Hurricane Milton highlight the significant role of human-caused climate change in exacerbating extreme weather events. The rapid intensification and strength of these storms can be attributed to the warming sea surface temperatures in the Gulf of Mexico, which are becoming increasingly influenced by climate change. By understanding the connection between climate change and extreme weather events, efforts can be made to reduce emissions, adapt to changing conditions, and mitigate the impacts of future storms. It is crucial to recognize the urgency of addressing climate change and taking action to protect our planet and communities from the growing risks of extreme weather events.