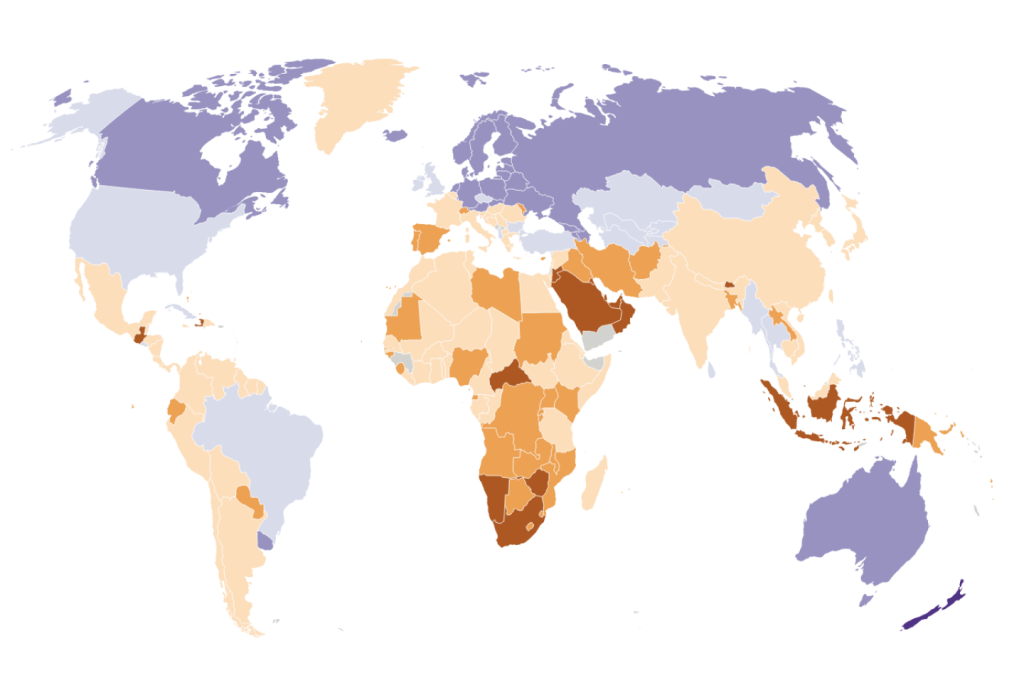
Eighty years ago, on April 21, 1944, French women were granted the right to vote through Article 17 of the French National Liberation Committee ordinance. This came much later than most other European countries, as well as pioneers like North American and New Zealand women who had acquired this right in the late 19th century. Across the world, women fought for decades to gain the right to vote, with countries like Finland, Uruguay, and Mongolia granting women voting rights in the early 20th century.
In France, activists like Olympe de Gouges began advocating for women’s voting rights as early as 1791. However, it was not until 1944 that French women finally gained the right to vote, after being excluded from the universal suffrage granted to men in 1848. Despite facing discrimination and being confined to the roles of wives and mothers, French feminists protested for nearly a century, seeking to dispel stereotypes of female incompetence in decision-making that prevented them from voting.
Historical trends show that when women gained the right to vote, it often coincided with significant societal changes in their respective countries. Major events such as the end of World Wars I and II, the collapse of empires, and the abolition of apartheid played a crucial role in advancing women’s suffrage. However, even when women were granted voting rights, it was not always extended to all women, often being contingent on factors such as social status, education level, age, and wealth. Indigenous women and women of color faced additional barriers to voting rights.
While progress has been made globally in granting women the right to vote, there are still countries where women continue to face significant obstacles. For example, Brunei remains a absolute monarchy where no one has electoral voice, while women in countries like Yemen and Afghanistan have lost the right to vote. In some countries, like North Korea, while women were granted voting rights in 1948, the options for voting are limited, showcasing how political regimes can impact democratic rights and freedom of choice.
Today, efforts are being made to acknowledge and celebrate the achievements of women in gaining voting rights, with a focus on creating a shared memory of feminism and the struggles of the past. The #metoo movement has sparked a renewed interest in the importance of gender equality and women’s rights, highlighting the need to remember and honor the activism and sacrifices of previous generations in the fight for gender equality. The quest for a more inclusive and equal society continues as countries strive to dismantle barriers to women’s participation in politics and decision-making processes.