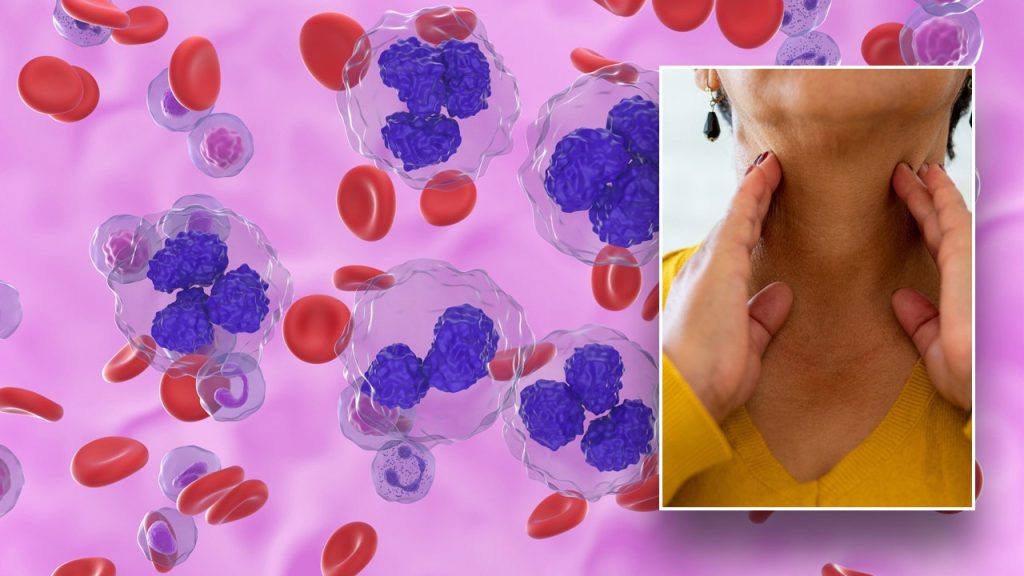
Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is an important part of the immune system. There are various types of lymphoma, with Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin being the most common. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for about 4% of all cancer cases in the United States. There are over 90 subtypes of lymphoma that have been identified by scientists to date.
Common symptoms of lymphoma include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, weight loss, fatigue, and swollen abdomen. Patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma may also experience additional symptoms such as drenching night sweats and unexplained weight loss. If experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor for further evaluation and potential next steps.
Treatment for lymphoma varies depending on the individual patient and the severity of the disease. Some patients may only require monitoring, while others may need chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiation therapy. In more severe cases, a bone marrow transplant or stem cell translation may be necessary. Both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma typically require similar treatment options.
While lymphoma can spread quickly, it is considered a highly curable type of cancer. Diagnosis may involve a physical exam and a biopsy to confirm the presence of lymphoma. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a positive outcome. Overall, lymphoma is a serious cancer, but with proper treatment and management, many patients are able to achieve remission and live fulfilling lives.